SaaS, or software as a service, is a type of cloud-based software delivery model in which a third-party provider hosts applications and makes them available to customers over the internet. This means that instead of installing and maintaining software on their own computers or servers, users can access the applications and their features remotely, typically through a web browser. SAAS has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its many benefits, including cost savings, scalability, and accessibility.
How does Software as Service Work?
To use a SaaS application, customers typically sign up for an account with the provider and pay a subscription fee, either on a monthly or annual basis. The provider then hosts the software on their own servers and makes it available to users over the internet, typically through a web-based interface.
Users can access the software and its features from any device with an internet connection, allowing them to work remotely and collaborate with others easily. Because the provider is responsible for maintaining and updating the software, users don’t have to worry about installing updates or patches, and can take advantage of new features and improvements as they are released.
Overall, SaaS offers a convenient and cost-effective way for businesses to access the software they need, without the expense and hassle of installing and maintaining it on their own computers or servers.
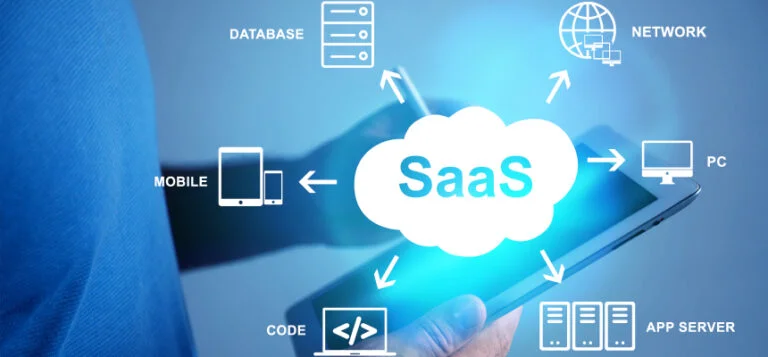
SaaS Architecture

https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/saas-concept-collage_26301280.htm
SaaS architecture typically consists of several key components, including the SaaS application itself, a web-based interface for accessing the application, a cloud-based infrastructure for hosting and delivering the software, and a payment system for managing subscriptions and billing.
- SaaS Application: The SaaS application is the core component of the architecture, and includes the features and functionality that users access and interact with. This may include a range of different tools and capabilities, such as document editing, project management, or customer relationship management.
- Web Based Interface: The web-based interface is the user-facing component of the architecture, and provides a way for users to access the SaaS application from any device with an internet connection. This interface is typically accessed through a web browser, and may include features such as login and authentication, user accounts and profiles, and the ability to access and interact with the application’s features and tools.
- Cloud-Based Infrastructure: The cloud-based infrastructure is the backbone of the SaaS architecture, and is responsible for hosting and delivering the SaaS application to users over the internet. This infrastructure typically includes a network of servers and other hardware, as well as the necessary software and tools for managing and maintaining the application.
- Payment System: Finally, the payment system is the component of the SaaS architecture that manages subscriptions and billing for the SaaS application. This may include features such as account management, subscription plans and pricing, and the ability to process payments and generate invoices.
Overall, SaaS architecture is a complex and interdependent system that enables the delivery of cloud-based software as a service over the internet. By leveraging the benefits of cloud computing and web-based interfaces, SaaS architecture provides businesses with a convenient and cost-effective way to access the software tools they need to operate and grow.
What are the Advantage of SaaS?
- Cost Savings: One of the key advantages of SaaS is cost savings. Because the software is hosted by the provider and accessed over the internet, customers don’t have to worry about purchasing and maintaining expensive hardware and infrastructure, which can be a significant expense for businesses. Additionally, because SaaS is typically subscription-based, businesses only pay for the software they use, rather than having to make a large upfront investment in licenses or hardware.
- Scalability: Another key advantage of SaaS is scalability. Because the software is hosted by the provider, customers can easily increase or decrease their usage as needed, without having to worry about purchasing additional hardware or making changes to their own infrastructure. This makes it a good option for businesses that are expecting to grow or shrink in the future, or for those with fluctuating needs.
- Accessibility: In addition to cost savings and scalability, SaaS also offers accessibility. Because the software is accessed over the internet, users can access their applications from anywhere with an internet connection, making it a convenient option for businesses with remote employees or multiple locations. This also means that businesses can access the latest versions of the software without having to install updates or patches, as the provider is responsible for maintaining and updating the software.
Overall, SaaS offers a number of advantages over traditional software models, including cost savings, scalability, and accessibility. For businesses looking to reduce their IT expenses and improve their productivity, SaaS can be a valuable option to consider.

https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/saas-concept-collage_26301286.htm
What are the Challenges and Risks of SaaS?
While SaaS, or software as a service, offers a number of advantages over traditional software models, it also comes with its own set of challenges and risks. These may include issues related to security, data privacy, vendor lock-in, and the potential for service disruptions.
- Security: One of the key challenges of SaaS is security. Because the software is accessed over the internet and data is stored on the provider’s servers, there is a potential for security breaches and data leaks. To address this, SaaS providers must implement robust security measures and regularly monitor and update their systems to prevent unauthorized access and protect user data.
- Data Privacy: Another challenge of SaaS is data privacy. Because user data is stored on the provider’s servers, there may be concerns about who has access to this data and how it is used. To address this, SaaS providers should have clear and transparent policies regarding data collection, usage, and sharing, and should be open and responsive to user inquiries and concerns.
- Vendor lock-in: A third challenge of SaaS is vendor lock-in. Because SaaS is typically subscription-based, businesses may become reliant on the provider for access to the software and its features. If the provider goes out of business or experiences a service disruption, this could leave businesses without access to the tools and capabilities they need to operate.
To mitigate this risk, businesses should carefully evaluate the financial stability and track record of potential SaaS providers, and should consider developing contingency plans in case of a service disruption. - Service disruptions: Because the software is hosted by the provider, businesses may be vulnerable to service disruptions if the provider experiences technical issues or other problems.
- Integration: Some SaaS applications may not easily integrate with other software or systems that businesses are using, which can limit their flexibility and functionality.
- Customization: Some SaaS applications may not offer the same level of customization as traditional software, which can be a disadvantage for businesses with specific needs or requirements.
Overall, while SaaS offers many benefits, it is important for businesses to carefully evaluate the challenges and risks associated with this model, and to choose a reputable and reliable provider to minimize these risks.
SaaS Trends
The SaaS, or software as a service, market is constantly evolving and changing. Some of the key trends in the SaaS industry include:
- Increased adoption: SaaS has become increasingly popular in recent years, with more businesses and organizations adopting SaaS solutions to improve their productivity and reduce their IT expenses.
- Expansion into new industries: SaaS is no longer just for traditional software applications, such as office productivity tools and CRM systems. It is now being used in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
- Increased competition: The SaaS market is becoming increasingly competitive, with more providers offering similar solutions and services. This has led to lower prices and more options for customers, but also greater pressure on providers to differentiate themselves and offer unique value.
- Focus on user experience: SaaS providers are increasingly focusing on the user experience, with an emphasis on user-friendly interfaces and intuitive design. This is aimed at making SaaS solutions more accessible and easy to use for a wider range of users.
- Integration with other technologies: SaaS providers are increasingly integrating their solutions with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the internet of things, in order to provide customers with more advanced and sophisticated capabilities.
Overall, the SaaS market is growing and evolving, and these trends are likely to continue in the coming years.
Feature image credit goes: https://www.freepik.com/free-photo/saas-concept-collage_26301287.htm
Leave A Comment